Vitiligo Treatment with NBUVB Phototherapy – Causes, Symptoms, Best Treatment Options
Vitiligo — often recognized by white patches on the skin — is a skin pigmentation disorder that affects millions worldwide. While it does not cause physical harm, vitiligo can have a deep emotional impact, affecting self-esteem and confidence.
Thanks to modern dermatology, advanced options like NBUVB phototherapy (Narrowband Ultraviolet B) are helping patients restore their natural skin colour, slow vitiligo progression, and regain confidence.
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition where melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) are destroyed or stop functioning. This leads to depigmented (white) patches that can appear anywhere — face, hands, arms, legs, scalp, lips and mouth.
It can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity.
Causes of Vitiligo
While the exact cause is unknown, vitiligo is believed to be an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks melanocytes.
Possible triggers include:
- Genetics – Family history of vitiligo or autoimmune conditions
- Autoimmune diseases – Such as thyroid disorders, type 1 diabetes, alopecia areata
- Skin injuries – Sunburn, cuts, or friction (Koebner phenomenon)
- Emotional stress – Can worsen or trigger vitiligo in some individuals
- Chemical exposure – Certain industrial chemicals may damage pigment cells
Types of Vitiligo
- Non-Segmental Vitiligo (NSV) – Symmetrical patches on both sides of the body; most common type
- Segmental Vitiligo (SV) – Usually appears at a younger age; affects only one side of the body
- Mucosal Vitiligo – Affects lips, mouth, or genital areas
- Focal Vitiligo – Small, localized patches without predictable spread
Common Symptoms
- White or light patches on the skin
- Premature graying of hair on the scalp, beard, eyebrows, or eyelashes
- Loss of pigment in mucous membranes (lips, mouth, nose)
- Mild itching before a new patch develops (in some cases)
How is Vitiligo Diagnosed?
Dermatologists use:
- Skin examination to assess the extent of pigmentation loss
- Wood’s lamp examination – A UV light that highlights depigmented areas
- Blood tests – To check for related autoimmune disorders
Early diagnosis is important for effective treatment.
Best Vitiligo Treatment Options
There is currently no universal “permanent cure” for vitiligo, but treatments can help:
- Repigment the skin
- Slow or stop progression
- Improve cosmetic appearance
Topical Medications
- Corticosteroid creams – Reduce inflammation and promote pigment return
- Calcineurin inhibitors – Safer for delicate areas like the face and neck
Light-Based Treatments
- Excimer laser – Focused UVB light for small, stubborn patches
- NBUVB phototherapy – Ideal for widespread vitiligo patches
Oral Medications
- Immunomodulators may be prescribed in fast-spreading vitiligo
Surgical Treatments (for stable vitiligo)
- Skin grafting – Transferring healthy skin to depigmented areas
- Melanocyte transplantation – Implanting pigment cells directly
Self-Care Tips for Vitiligo Patients
- Apply sunscreen daily – Protects depigmented skin from burns and reduces contrast
- Avoid skin trauma – Cuts, burns, or friction can trigger new patches
- Eat a balanced diet – Include vitamin B12, zinc, copper, and folic acid
- Manage stress – Through meditation, yoga, or hobbies
- Stay consistent with treatment – Vitiligo management requires patience
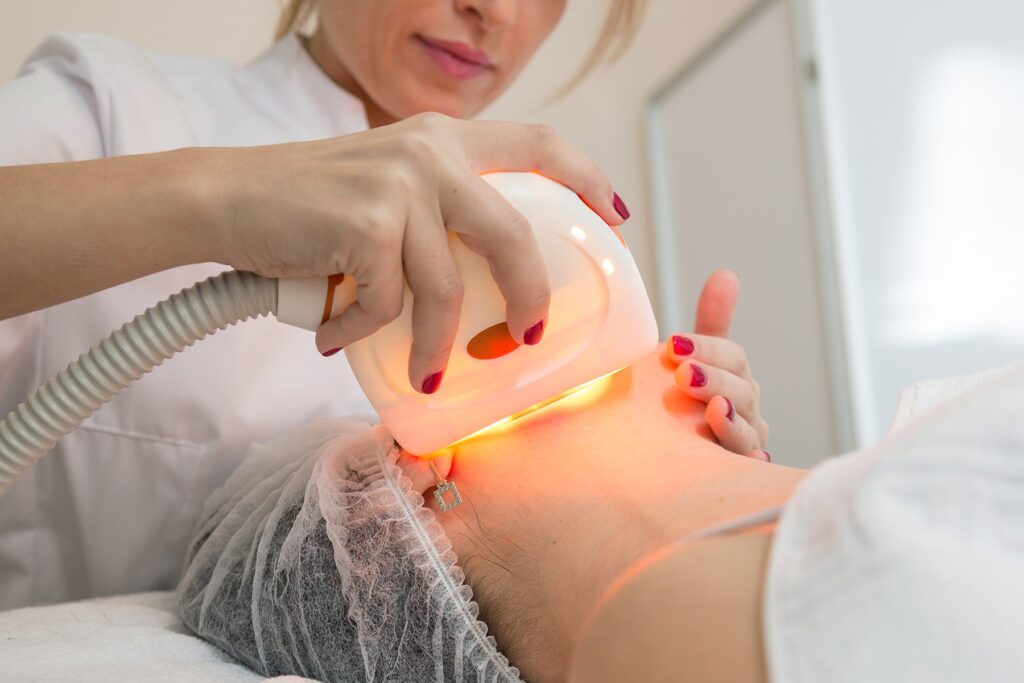
NBUVB Phototherapy – Shining Light on Hope for Vitiligo
Narrowband Ultraviolet B (NBUVB) phototherapy is considered the gold standard for treating vitiligo in both children and adults.
It works by delivering UVB light at a specific wavelength (311–313 nm), stimulating melanocytes and encouraging melanin production in depigmented skin.
Why NBUVB is a top choice:
- Safe for all ages – Even children can undergo treatment
- Treats large areas efficiently
- Minimal side effects compared to older therapies
- Visible improvement in 2–3 months for many patients
- Can be combined with topical treatments for better results
Treatment process:
Patients either stand in a phototherapy chamber or receive targeted light treatment for specific areas. Sessions are painless, quick, and typically done 2–3 times a week under dermatologist supervision. There’s no downtime — you can resume daily activities immediately.
With consistent sessions, NBUVB phototherapy can restore skin color, slow disease progression, and dramatically boost self-confidence.
FAQs
- Can vitiligo be cured permanently?
Currently, there is no guaranteed permanent cure, but many treatments — especially NBUVB phototherapy — can restore pigment and control progression for long periods.
- How many NBUVB sessions are needed for vitiligo?
Most patients start noticing improvement in 2–3 months, with continued progress over 6–12 months of regular treatment.
- Is NBUVB phototherapy safe?
Yes. It is one of the safest light-based treatments for vitiligo, with minimal side effects when done under dermatologist supervision.
- Is vitiligo contagious?
No. Vitiligo is not infectious and cannot be spread through touch or close contact.
- Can diet help in vitiligo?
While no diet can cure vitiligo, nutrient-rich foods containing vitamin B12, folic acid, copper, and zinc support skin health and overall immunity.
- Is vitiligo genetic?
Genetics can play a role — having a family member with vitiligo or other autoimmune diseases increases your risk.
- Can stress make vitiligo worse?
Yes. Stress can trigger autoimmune reactions and worsen vitiligo in some individuals.
Conclusion
Vitiligo is a medical condition — not a flaw. With early diagnosis and modern treatments like NBUVB phototherapy, patients can achieve visible re pigmentation and improved quality of life.