Fungal Infections – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention
Introduction
Fungal infections are among the most common skin problems worldwide. While they might start as a mild rash or itching, they can quickly spread and become stubborn if not treated properly.
One of the biggest mistakes people make is self-medicating with over-the-counter creams, especially those containing steroids. These may temporarily reduce itching but actually allow the fungus to grow and spread. The safest and fastest way to recover is to consult a dermatologist at the earliest sign of symptoms.
What is a Fungal Infection?
A fungal infection occurs when certain fungi multiply on the skin, scalp, or nails. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can affect various body areas such as:
- Groin and inner thighs
- Feet (especially between toes)
- Armpits and skin folds
- Nails
- Scalp
Why Early Dermatologist Consultation Matters
- Accurate diagnosis – Not every rash is fungal; wrong treatment can worsen the condition.
- Right medication from the start – Prevents spread and resistance.
- Faster recovery – Avoids weeks or months of prolonged treatment.
- Lower risk of complications – Stops chronic recurrence and secondary infections.
Common Types of Fungal Infections
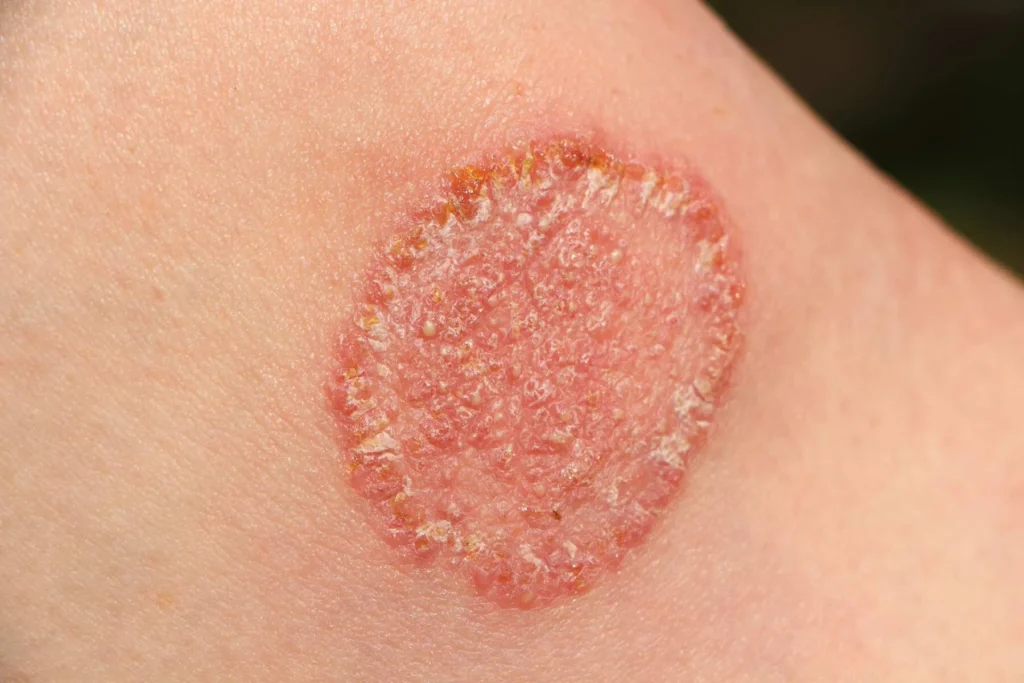
- Ringworm (Tinea corporis) – Circular, red rash with central clearing.
- Athlete’s Foot (Tinea pedis) – Peeling, itchy skin between toes.
- Jock Itch (Tinea cruris) – Red rash with itching in the groin area.
- Fungal Nail Infection (Onychomycosis) – Thick, brittle, discoloured nails.
- Scalp Ringworm (Tinea capitis) – Hair loss patches, mostly in children.
Symptoms of Fungal Infections
- Persistent itching or burning
- Red, inflamed patches
- Scaling or flaking skin
- Blisters or small bumps
- Nail thickening or discoloration
- Hair loss in affected areas
The Risk of Self-Medication
Many pharmacy creams contain steroids mixed with antifungals, which:
- Suppress symptoms temporarily but let fungus spread deeper
- Cause skin thinning and damage
- Make the infection resistant to standard treatments
Bottom line: Avoid self-medicating and seek professional treatment early.
Diagnosis by a Dermatologist
- Visual examination of the affected area
- Microscopy of skin scrapings or nail clippings
- Fungal culture to identify the specific fungus
Treatment Options
- Topical Antifungal Creams – Clotrimazole, Terbinafine, Ketoconazole (prescribed after confirmation).
- Oral Antifungal Medicines – For severe, widespread, or nail/scalp infections.
- Medicated Shampoos – For scalp fungal infections (Ketoconazole, Selenium Sulfidic).
⚠ Avoid steroid-containing creams unless prescribed for another condition by a dermatologist.
Prevention Tips
- Keep skin dry, especially after bathing.
- Wear loose, breathable cotton clothing.
- Change sweaty clothes quickly.
- Avoid sharing towels, footwear, or grooming tools.
- Use antifungal powder in hot, humid weather.
- Manage blood sugar if diabetic.
FAQs
1.How soon should I see a dermatologist if I have symptoms?
Immediately. Early consultation leads to faster recovery and prevents spread.
2.Can I treat a fungal infection at home?
Home remedies may give mild relief but are rarely enough for complete cure. Professional treatment is more effective.
3.Are fungal infections contagious?
Yes, they spread through direct contact or sharing personal items.
4.How long does treatment take?
Mild cases may clear in 4-6 weeks. Nail and scalp infections can take months.
5. Why do fungal infections keep coming back?
Common reasons include incomplete treatment, poor hygiene, re-exposure to fungus, and uncontrolled diabetes.
Key Takeaway
Fungal infections are treatable, but self-medication delays recovery and increases risks. At the first sign of itching, redness, or rash, visit a dermatologist for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Early care means faster healing, less discomfort, and reduced chances of recurrence.