Psoriasis Treatment: Causes, Symptoms, and the Role of Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) Phototherapy
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches. Learn about psoriasis causes, symptoms, treatment options including Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy, topical creams, oral medications like Apremilast, biologics, and lifestyle management.
What Is Psoriasis?
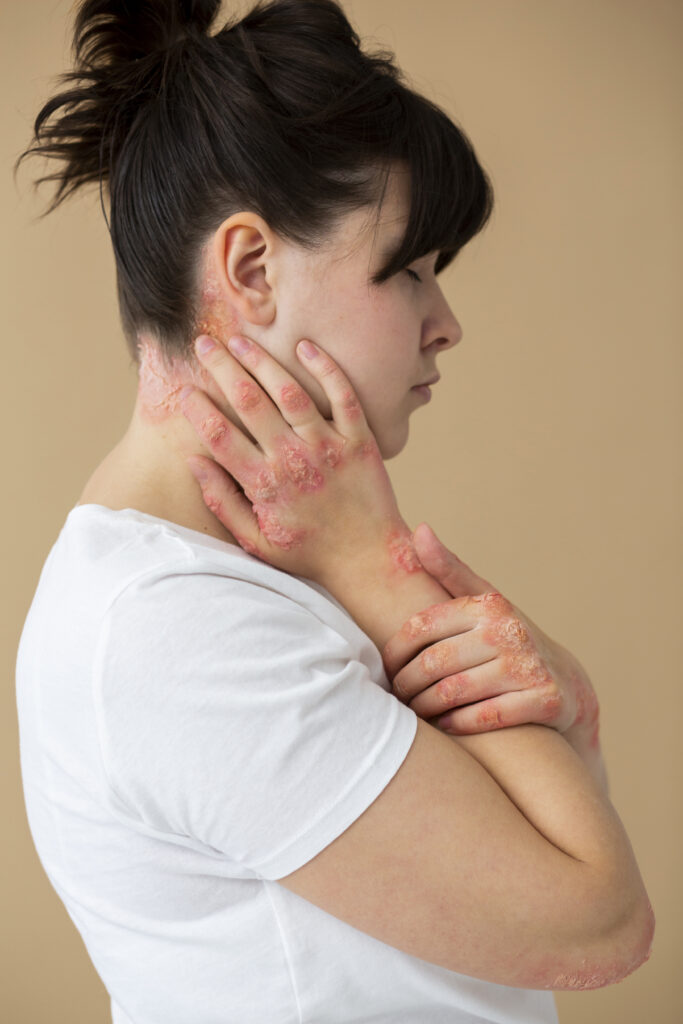
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that speeds up skin cell turnover, leading to red, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin. These lesions most commonly appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
Although psoriasis is not contagious, it can be physically uncomfortable and emotionally distressing, significantly impacting daily life.
Types of Psoriasis
- Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris): The most common form, with raised red plaques and silvery-white scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Appears as small, drop-shaped spots, often triggered by infections.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Smooth, shiny red lesions in skin folds (groin, armpits).
- Pustular Psoriasis: White pustules filled with pus on inflamed skin.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare, severe form that causes widespread redness and scaling.
Psoriasis Causes and Triggers
Psoriasis develops when the immune system over-activates T-cells, mistakenly attacking healthy skin cells. This leads to inflammation and rapid skin growth.
Common triggers include:
- Stress and anxiety
- Skin injury or trauma
- Strep throat and other infections
- Cold or dry weather
- Alcohol and smoking
- Medications (such as beta-blockers, lithium, antimalarials)
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
There is no permanent cure for psoriasis, but a wide range of effective treatments can control symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve quality of life.
- Topical Treatments for Psoriasis
Best suited for mild cases or as combination therapy:
- Corticosteroid creams: Reduce inflammation and itching.
- Vitamin D analogs (Calcipotriol): Slow down skin cell growth.
- Coal tar and salicylic acid: Reduce scaling and soften thick plaques.
- Topical retinoids (Tazarotene): Help normalize skin turnover.
Advantages: Easy to apply, minimal systemic side effects.
Limitations: Less effective for widespread or severe psoriasis.
- Oral and Injectable Systemic Medications
For moderate to severe psoriasis, systemic medications are prescribed when topical treatments alone are insufficient.
- Methotrexate: A long-established treatment that suppresses the immune system to control inflammation.
- Cyclosporine: Provides fast relief during severe flare-ups but usually for short-term use.
- Acitretin (oral retinoid): Helps normalize skin growth, effective for pustular and severe plaque psoriasis.
- Apremilast (Otezla): An oral PDE4 inhibitor that reduces inflammation by targeting intracellular signaling pathways. It is convenient (oral pill), does not require frequent blood tests, and is effective in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Possible side effects include gastrointestinal upset and weight loss.
- Biologics (injectable therapies): Modern targeted medicines that block specific immune pathways, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors. They are highly effective for severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Pros: Effective for moderate to severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Cons: Require regular monitoring, possible immune suppression, cost considerations.
- Phototherapy for Psoriasis
Phototherapy (light therapy) is a non-invasive treatment where controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light reduces psoriasis symptoms. The most effective and commonly used type is Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy.
How NB-UVB Phototherapy Works
- Uses a specific wavelength (311–313 nm) of UVB light.
- Reduces inflammation by calming immune system activity.
- Slows abnormal skin cell growth.
- Promotes remission periods where symptoms remain controlled.
NB-UVB Treatment Protocol
- Administered 2–3 sessions per week.
- Requires 20–36 sessions for noticeable improvement.
- Available in dermatology clinics; home phototherapy devices may be prescribed in select cases.
Advantages of NB-UVB Phototherapy:
- Safe for children and pregnant women under supervision.
- Effective for plaque, guttate, and inverse psoriasis.
- Fewer systemic risks compared to oral medications.
Possible Side Effects:
- Mild redness similar to sunburn
- Temporary itching or dryness
- Rare long-term risks with prolonged overuse
- Lifestyle and Home Care for Psoriasis
Lifestyle changes and supportive care can complement medical treatments:
- Moisturize daily to reduce dryness and scaling.
- Manage stress with yoga, meditation, or breathing exercises.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory foods.
- Avoid triggers such as alcohol, smoking, and harsh skincare products.
FAQs
1: Can psoriasis be cured?
No, psoriasis cannot be cured, but treatments like NB-UVB, Apremilast, biologics, and lifestyle management can keep it under control.
2: How long does NB-UVB phototherapy take to work?
Most patients notice improvements within 10–12 sessions, with best results after 20–30 sessions.
3: Is Apremilast safe?
Yes, Apremilast is generally safe, especially compared to stronger immunosuppressants. It does not require frequent lab monitoring, though some patients may experience mild side effects like nausea or weight loss.
4: Which treatment is best for me?
The right treatment depends on psoriasis type, severity, and individual health conditions. A dermatologist can create a personalized treatment plan combining creams, tablets, phototherapy, or biologics.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a chronic but manageable condition. Advances in treatments such as Narrowband UVB phototherapy, Apremilast, and biologics have transformed care, offering effective symptom control and long-term relief.
With the right combination of medical therapy, lifestyle changes, and regular dermatology follow-up, most patients can lead a comfortable and confident life despite psoriasis.